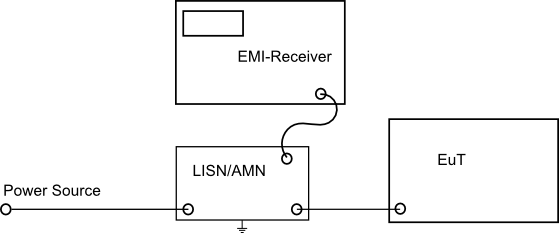
LISN Line Impedance Stabilisation Networks / AMN Artificial Mains Network
A LISN Line Impedance Stabilization Networks / AMN Artificial Mains Network
- supplies the neccessary mains voltage (AC or DC) and current for the Equipment under Test (EuT).
- couples interference voltage generated by the EuT and supplies it to the receiver.
- provides well defined RF-impedance to the Equipment under Test (EuT)
- keeps away unwanted disturbance coming from mains (filter)
- protects the mains from unwanted disturbance voltage generated by the EuT
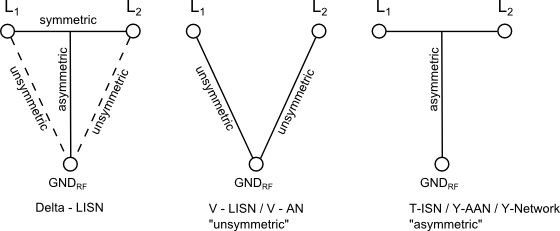
- We can distinguish three types of LISN: V-, T- and Delta-LISN
Figure 2 shows the voltage relationship of a two-line-system with separate ground.
The V-LISN measures the unsymmetric disturbance voltage between the two lines L1 and ground or L2 and ground respectively. V-LISN are also called V-ANM (Artificial Mains Network). The V-LISN is by far the most commonly used LISN.
There are two types of V-LISN with different impedances. The V-LISN with a 5μH inductance (CISPR 16-1-2, CISPR 25, ISO 7637, DO160) are normally used to measure equipment for vehicles, boats and aircrafts connected to onboards mains with DC or 400 Hz. The other Type of V-LISN with 50 µH according to CISPR 16-1-2, MIL STD 461 and ANSI C63.4 is intended to operate at mains frequencies of 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
The T-ISN (Figure 2 right) measures the asymmetric disturbance voltage (common mode voltage) and provides it to an EMI Receiver. T-ISN is normally used for measuring telecommunication and data transmission equipment connected to symmetrical lines as e.g. twisted pairs.





 line ID :
line ID :